Week of March 16
Welcome to a new topic! It is a very charged one!
Electric Charge and Static Electricity!
 |
Big Idea - Forces between objects act when the objects are in direct contact or when not touching
I can...
Vocabulary: electric charge, static electricity,
electrical
conductor, electrical insulator, semiconductor, electrical field
and force, induction, current
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
What is electrical charge?
 |
- Electric charge involves electromagnetic interactions between particles of matter
- Matter can be overall negatively, positively, or neutrally charged by the loss or gain of negative electrons
- Charged objects exert a force on each other even if they are not touching - this is called electric force
- How strongly the electric force pushes or pulls depends on the amount of charge and the distance between the objects
- Charging objects involves moving negative electrons from one object to another - but they are not lost - just moved
- Electric charge is always conserved - this means that the total amount of charges always remains the same - they just trade places
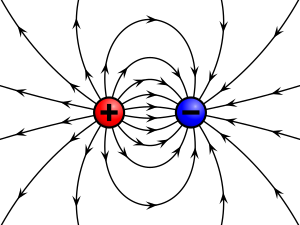
- Objects with the same charge (like charges) - repel each each other
- Objects with different charges (unlike charges) - attract each other
- The closer the charged objects are, the stronger the electric force

How Do Objects Become Charged?
- Objects become charged when they gain or lose electrons
- This can happen 3 ways: friction, contact, induction (charges are rearranged int he object without touching it)
What is Static Electricity?
 |
You guessed it! The best example of static electricity is lightning! |
- During storms or windy conditions, negative charges (electrons) build up in the bottom of clouds due to friction mostly
- When enough negative charges build up, they induce or induction occurs and electric discharge happens in the form of lightning
Conductor and Insulators
- Some materials are better conductors of electricity than others
- Most metals like copper are very good conductors - meaning they allow the charges to move freely
- Other materials like plastics, rubber, and wood are not good conductors - but they are used to insulate metals that conduct electricity - this stops a lot of shocks and electrical fires!
- Semiconductors are a special type of conductor used in computer chips - their main material is silicon
- Semiconductors conduct electricity better than insulators but not as well as a material like copper - but they are perfect for usage in electronics
Links:
No comments:
Post a Comment