Week of October 21-October 28
What is Plate Tectonics?
Workbook p. 182-203
I can's...
BIG IDEA!
The Earth's crust consists of tectonic plates that move relative to each other changing the surface of the Earth over time.
I can's...
- explain the theory of plate tectonics
- describe the evidence that supports the theory of plate tectonics?
- I can explain that there are three types of stresses related to the movement of the plates?
- describe and relate the three main hypotheses that explain how the tectonic plates move?
- relate how plate tectonics affects society and science?
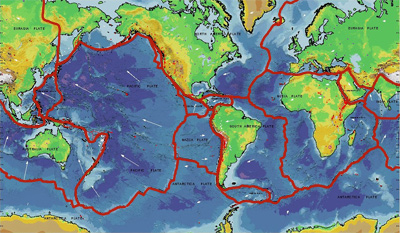
- investigate the relationships between plate boundaries and and geological features and events using maps
- describe and model the three different types of plate boundaries?
- describe what type of landforms or geological events are associated with the different types of plate boundaries?
What evidence supports the theory of plate tectonics?
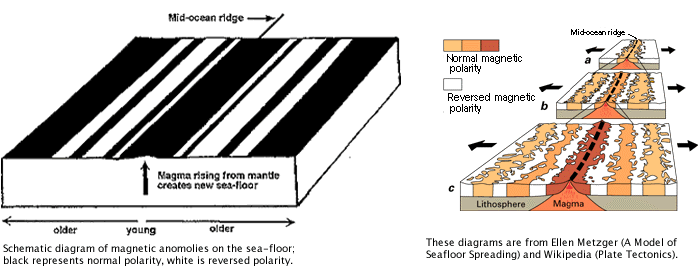
1. Sea-Floor Spreading

2. Magnetic Field Reversals

3. Locations of earthquakes, volcanoes, and folded mountains

What causes tectonic plate motion?

Question: What are the 3 processes that are responsible for moving the tectonic plates?
How do the tectonic plates shape the Earth's surface?
Here are the forces or stresses involved that deform the Earth's crust:

Where do these stresses occur?
What are the 3 types of plate boundaries?

Question: Can you match stresses to the plate boundary they occur at?
What are some examples of landforms created by these different plate boundaries?
Convergent Plate Boundary

Himalayan Mountains
Divergent Plate Boundary

The Great African Rift Valley


Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Transform Plate Boundary

San Andreas Fault - California
Links:
Landforms at Plate Boundaries - Animation
Ring Of Fire Video
Hawaiian Volcanoes - Video
Activity - How Fast Do the Plate Move? - Complete Questions on Slides 1-4
Activity - Under Yellowstone
Yellowstone Super Volcano Video
Ring Of Fire Video
Hawaiian Volcanoes - Video
Activity - How Fast Do the Plate Move? - Complete Questions on Slides 1-4
Activity - Under Yellowstone
Yellowstone Super Volcano Video