Week of March 23
Magnetism!
Big Idea: Forces between objects act when the objects are in direct contact or when not touching.
I can...
- Build and electromagnet to investigate magnetic properties and fields
- Explain how generators and motors produce their own magnetic field when an electric current flows through it
Magnetic Force - feel the push and pull!

What makes some materials magnetic and some not magnetic?

- Iron, nickel, and cobalt are the top 3 materials that have magnetic properties
- Materials are magnetic due to spinning electric charges
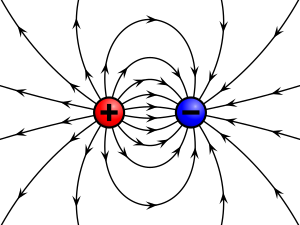
- Magnetic force can act at a distance - just like gravity and electrostatic force
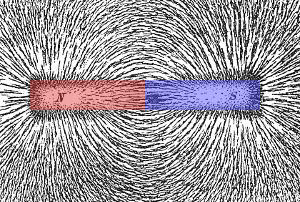
- Magnet have poles - a north pole and a south pole
- Unlike poles attract - like poles repel
Magnetic Field - the area surrounding a magnet
Magnetic charge flows from north to south; the magnetic force is strongest at the poles
The Earth is a Magnet!
The Earth's Magnetic Field

What does our magnetic field have to do with auroras?

What is going on inside magnetic materials?
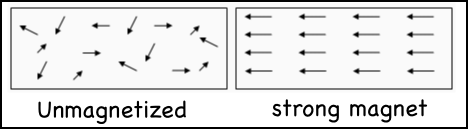
- Whether a material is magnetic or not depends on the type of atom the material is made of
- As an electron moves around an atom, it makes an magnetic field - in substances like iron - a north and south pole are created
- In a substance like copper, the magnetic fields cancel each other out and therefore it is not magnetic
- In substances like iron, nickel, and cobalt, the north and south poles form areas called domains
- If the domains can line up, then the material can be become magnetic or be temporarily magnetized
Types of Magnets
1. Ferromagnets - these are materials that can be turned into magnets

2. Temporary Magnets

- Some materials can be magnetized for a short period of time - the domains line and it becomes a magnet
3. Electromagnets

- Electromagnets use an electric current to create a strong magnetic field that can be turned off and on
- Electromagnets are used to pick up heavy materials like scrap in a junkyard

- Electromagnetism results when an electric current and magnetic field interact
- When a magnetic field creates an electric current in a wire it is called electromagnetic induction
- Electromagnets are used in motors
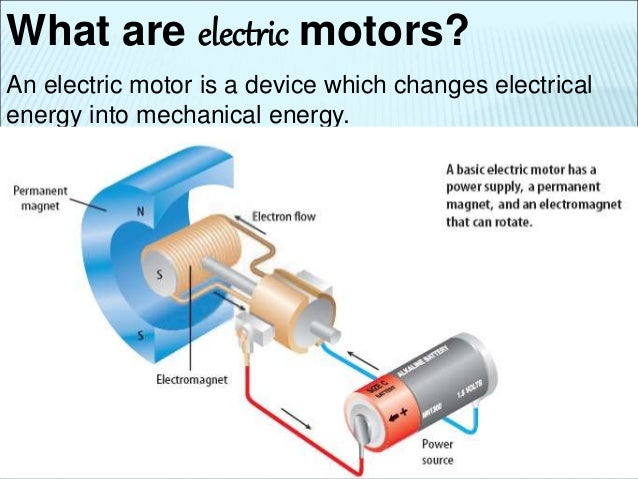
- Electric generators use induction to change mechanical energy to electrical energy
How an electric generator works

Magnets and Electromagnets Interactive